RISK – Ground collapse and engulfment
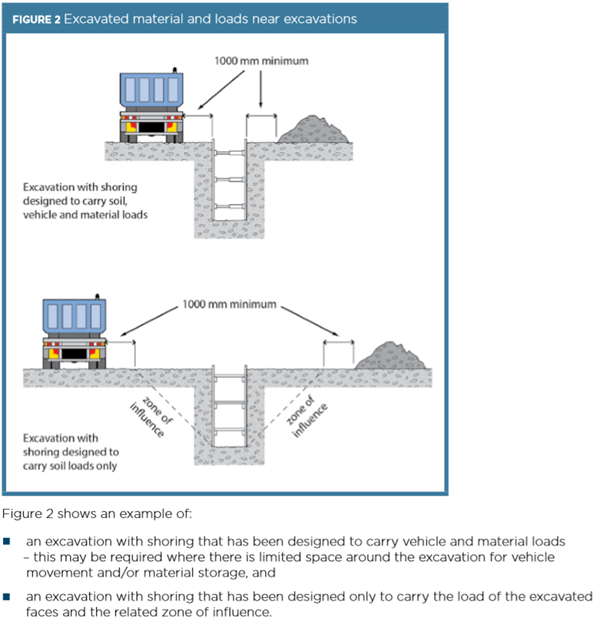
An excavation’s zone of influence refers to the volume of soil around an excavation that can be affected by any external load. The zone is usually measured as 45 degrees out from the bottom of an excavation.
Whilst the zone of influence is usually measured as 45 degrees out from the bottom of an excavation, this may change depending on the soil type and weight of the material/vehicle.
Mechanical plant, vehicles, storage of materials (including excavated material) or any other heavy loads must not be located in the zone of influence of an excavation as this will place additional load onto that area.
As a general rule, it is best practice to place all loads and barricades at least 1m back from the zone of influence.
 Excavation Safety Guide. Worksafe New Zealand
Excavation Safety Guide. Worksafe New Zealand
The zone of influence will depend on the ground conditions. It is the zone in which there may be an influence on the excavation, including possible ground collapse.
Where the ground around the excavation may be affected by any external load, a Geotechnical Engineer must determine whether protective systems (as per GMR 2.1) needs to be designed and installed to accommodate the additional load.
If spoil is placed close to an excavation due to obstructions like fences, buildings or trees, the weight of the spoil may overload the excavation face and cause the excavation to collapse.
If materials cannot be placed outside the zone of influence due to limited space, a ground support (or protective) system must be designed and installed to carry the additional load.
Model Code of Practice for Excavation Work. Safe Work Australia
Consider also, the excavations zone of influence on the stability of any nearby structures and make sure the excavation does not remove any ground support from these structures

Shafts
In regard to shafts, consideration must also be given to additional loadings such as:
- barriers/edge protection on the shaft top
- cranage on the shaft or excavation side walls
- construction space-proofing to ensure loads can pass freely
Any further loads imposed on these systems (such as man riders and hoists) must be factored into the overall design.


Refer to the Excavation Material and Loads near Excavations section of the Excavation and Trenching Procedure (linked below) for further information
