RISK – Trench / Tunnel collapse. Engulfment
In Victoria, no vertical side of an excavation is to exceed 1m in height.
Stairways, ladders or ramps must also be provided in excavations that are 1.2 metres or more in depth and located in positions that a worker will not be required to travel laterally more than 10m, from any point within the excavation.
In extremely large excavations where it is not practical to provide a stairway, ladder, or ramp every 10m, they must be placed in locations of easy access and provide a safe means of egress. All stairways and ramps will be equipped with standard handrails and toe-boards where applicable.
Ramps used for foot traffic within the job should be no steeper than 1:6 unless cleats are used and in no case steeper than 1:4 gradient. To climb a steeper grade than this, flights of steps alternating with landings should be used.
All ladders must extend a minimum of 900mm above the surface and be secured by tying off or by a worker holding the ladder. All structural ramps or runways used for access/egress of workers and/or equipment must be designed by a qualified person and inspected by the works supervisor prior to use.
Keep the bed of the excavation clear of anything that would impede a workers’ safe egress in an emergency, including:
- Debris
- Loose spoil
- Timber
- Tools
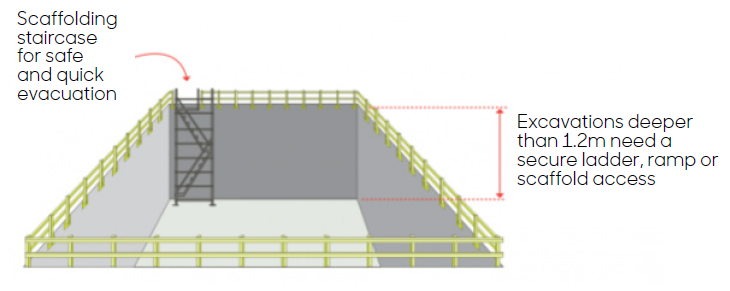 Scaffold staircase for a safe and quick evacuation.
Scaffold staircase for a safe and quick evacuation.
Excavation Safety Guide. New Zealand
For further information of protective systems such as benching, battering or shoring, refer to the guidance in GMR 2.1
Access to tunnels
Access to unsupported ground must be controlled within the Permit to Tunnel (PTT). Access will not be permitted until controls are in place. The definition of supported ground will be defined within the permit.
Access to areas of unsupported ground will be prevented by:
- Briefing work crews on the PTT conditions and restrictions
- Clearly defining "unsupported ground" and the criteria for re-entry in the ground-support design report
- Installing barricading and signage to prevent unauthorised access.
- Identifying and communicating a designated point of contact for access.

Emergency planning for tunnelling works
A register, sign on sheet or tag in / tag out system must be maintained during underground works to ensure the personnel numbers are controlled and known in case of an emergency.
An emergency plan must be in place and agreed with the emergency services prior to underground works commencing. This must include:
- Senarios of shaft/ tunnel fire incidents. For example, for TBMs this will include the use of self rescue systems and rescue chambers.
- Key responsible people and lines of reporting
- Recovery scenarios.
- Frequency of emergency evacuation drills
Emergency Plans must be reviewed and updated as required to include current access routes and any changes to the muster point.
All changes to the Emergency Plan must be communicated to all relevant stakeholders.
Air quality & ventilation for underground works
- Review of respiritory silica levels to be carried out and exposure levels understood. This will in turn dictate the ventilation / extraction design and specify PPE required.
- Ventilation systems must comply with relevant regulations in regard to minimum airflow and air-volumes and maximum allowable respirable dust levels.
- Ventilation systems must be designed by a competent Engineer and must be capable of delivering clean air or extracting exhaust air to the full cross section of the shaft and tunnel at the regulated rates.
- A ventilation and gas monitoring system must be designed, installed, certified and maintained by a competent person. The monitoring system must immediately alert if the level of oxygen and toxic gases does not meet Workplace Exposure Standards
- Diesel engines must be fitted with a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) system that is suitable for use on vehicles/plant operating in an underground environment
- Diesel operated plant shall be replaced by electric driven plant where reasonably practicable
Related GMRs
2.1 Assess excavation design requirements and implement appropriate protective systems
Related Procedures / Forms
Excavation and Trenching Procedure
Permit to Tunnel
